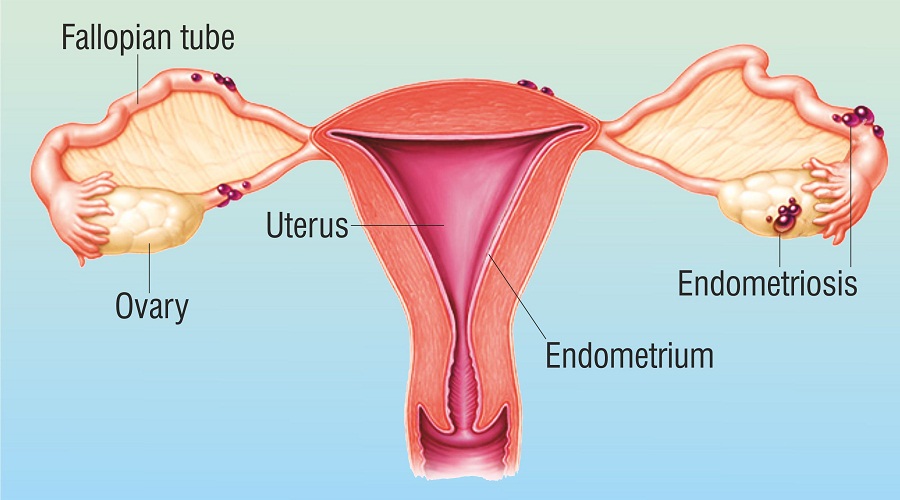
Also known as endometrioma, chocolate cyst is one of several types of cysts on ovaries. A chocolate cyst is a sac or pouch growing on the ovary that contains fluids and sometimes semi-solid material too, in which case it may be referred to as a complex ovarian cyst. In simple words, a chocolate cyst is a blood-filled cyst found in the ovaries.
Many women are affected by chocolate cyst at some point in their lives usually before menopause. Endometrioma is one of the estrogen-dependent gynecological diseases affecting about 5% to 10% of women of reproductive age .
Chocolate Cyst: How Does It Form?
A chocolate cyst forms when an endometrial tissue (tissue from the inside surface of your uterus) abnormally attaches and grows in the ovaries, as it can with endometriosis. These patches of endometrial cells may form small cysts that multiply into even more cysts when stimulated by menstrual hormones. In the event of no pregnancy, the endometrial tissue usually breaks up from the body during menstrual bleeding. However, in the case of endometriosis, this doesn’t happen and instead, the blood accumulates and irritates the surrounding tissue.
Why Is It Called Chocolate Cyst?
The endometrial tissue inside the ovarian cyst responds to monthly hormones. This tissue bleeds and fills the interior of these cysts with un-clotted blood. Chocolate cysts get their name from dark old blood which is black, tarry and thick, grossly resembling chocolate. Other names for chocolate cyst are endometrial cyst, endometrioma cyst, and chocolate ovarian cyst.
Symptoms Of Chocolate Cyst Or Endometrioma
The symptoms of chocolate cyst are similar to those of endometriosis since the underlying disease is the same, but all cases are individual. As with most conditions, we all react differently. With cysts, some women, regardless of how long the cysts have been present, will have severe symptoms while other women will have little or no symptoms at all. Thus, the extent and severity of symptoms do not always correlate with how far endometrioma has progressed.
Some of the most common symptoms of endometrioma are:
- Abdominal cramping/swelling during the menstrual cycle
- Abnormal bleeding/spotting
- Painful periods
- Excessive vaginal bleeding
- Dark-coloured vaginal discharge
- Pain when going to the toilet—both urinating and emptying the bowels
- Pain during sexual intercourse and
- Pain during exercises, such as bending and stretching
Intense, sharp pain may indicate that the cyst has pressed on the ovary and this has caused it to twist and cut off the blood supply.
Chocolate cyst rupture can also be a source of severe pain. If a chocolate cyst ruptures, the contents may spill out onto the ovaries and other organs of the pelvis. This can lead to complications such as adhesions (scarring), infection, and intense pelvic pain. A ruptured ovarian cyst can be a serious medical emergency. You should consult an expert immediately if you have symptoms like excessive bleeding, fever, vomiting or severe pain.
Some other conditions that mimic this disease include ovarian cysts, Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), and ectopic pregnancy. Ectopic pregnancy or tubal pregnancy is a complication when the pregnancy grows outside of your uterus.
How Does Chocolate Cyst Impact Fertility?
Many women are interested in knowing if a chocolate cyst will prevent or interfere with pregnancy. It is possible for a woman to still get pregnant even without removing the cyst. The odds of being fertile are very good if there is only one chocolate cyst and it is small in size. The answer is not so clearcut in more advanced cases in which multiple chocolate cysts are present and some are larger than a few inches in diameter. Here are some ways in which endometrioma can affect fertility:
- Chocolate cyst growing on the ovary can prevent the ovary from forming eggs, which are to be fertilized.
- In some cases, eggs may release from the ovary of a woman with chocolate cyst, but sperm cannot penetrate the walls of these released eggs.
- Due to the presence of chocolate cyst, the fallopian tubes may develop scarring. This, in turn, may interfere with the transport of the egg and the sperm.
- Apart from this, chocolate cyst can also cause a greater risk of ectopic or tubal pregnancy in affected women.
- Moreover, there may also some other substances present in chocolate cysts that may prevent fertilization of the egg.
- Chocolate cysts are affected by reproductive hormones and thus there may be an imbalance of these reproductive hormones. This, in turn, can prevent a fertilized egg from implanting into the uterine wall and may cause miscarriage.